Waste batteries is sent to specialized treatment plants located within a 300 km radius around Luxembourg and then sorted into different categories according to their chemical composition (lithium, nickel-cadmium, etc.).
Some batteries contain toxic heavy metals (like cadmium, lead or mercury) that must be treated in accordance with environmental regulations to prevent soil and water contamination.
Other metallic components found in batteries such as iron, zinc, or aluminum are highly recyclable and can be reused in various industries.
For example:
• Ferromanganese, recovered from the metal casing of certain batteries, can be reused in foundries to manufacture faucet components or railway tracks.
• Zinc powder, extracted from saline or alkaline batteries, can be used to produce gutters, zinc components or anti-rust paint.
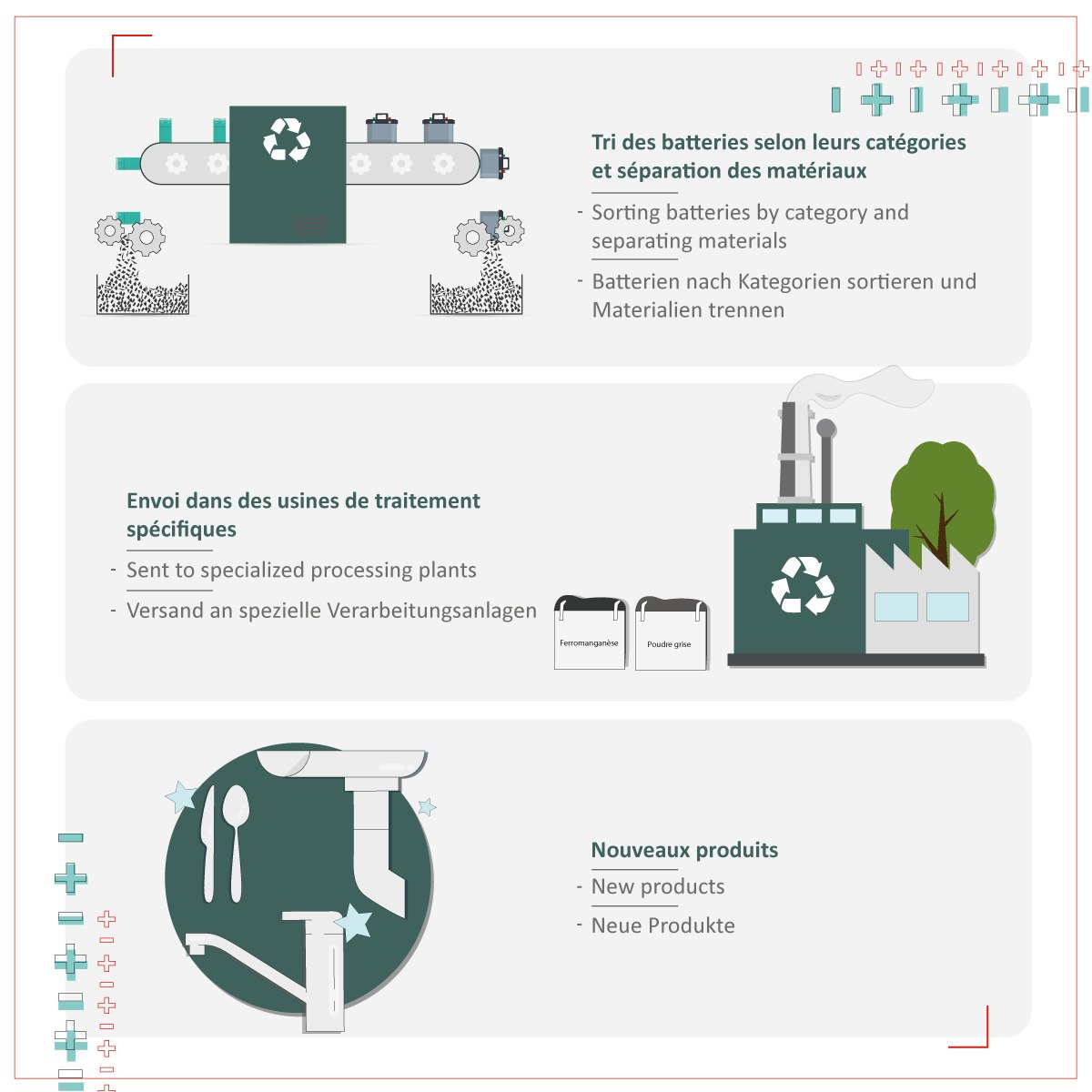
Battery recycling not only reduces the environmental impact of hazardous waste but also reintroduces critical and costly materials into the circular economy reducing reliance on raw material extraction.
